Dark Core Personality Test: Ensuring a Safe & Productive Workplace

What have we covered
TL;DR
- The dark core personality test identifies underlying negative traits influencing manipulative or unethical behavior.
- This test measures the shared psychological core behind traits such as narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy.
- Understanding dark personality traits supports better recruitment, leadership assessment, and behavioral prediction.
- Platforms like Skillrobo use dark core personality tests to evaluate integrity and psychological fit in workplaces.
Dark Personalities at the Workplace – Watch Out for These Traits
The Narcissist – Spotlight seeker
Thrives on self-admiration, dominates meeting discussions, dismisses peer/team lead feedback, makes teammates feel undervalued
Machiavellian – Strategic Manipulator
Appears politically skilled, plays colleagues against one another, manipulates team members, loses trust of coworkers
Psychopath – Reckless risk taker
Makes aggressive decisions, displays reckless behavior, ignores long-term effect of decisions, practices emotional detachment
Sadist – Enjoyer of Discomfort
Derives subtle satisfaction from public corrections, enjoys seeing others struggle, creates pressurized work environments
Egoist – Self-first Performer
Prioritizes self recognition over team success, redirects credit toward themselves, resists feedback, and makes decisions for personal gain
Unveil dark personalities with personality assessments from Skillrobo
A safe and productive workplace requires the right mix of technical and soft skills. Evaluating potential candidates for their technical competencies is the most common pre-employment assessment that most employers focus on. However, personality assessments are equally important to build a harmonious work environment. Furthermore, personality assessments should assess positive and negative attributes in candidates.
Dark traits in candidates, such as manipulation, deceit, entitlement, and moral indifference, can significantly influence how people behave in social or professional environments. The dark core personality test helps identify these traits during the pre-employment screening process. HR teams and employers can use the dark core personality test to measure the hidden psychological tendencies behind these negative traits.
What is the dark core personality test? Why do you need the dark personality test? How does this assessment work? Are the dark core and dark triad tests the same? Discover answers to all these questions and explore the negative traits test in detail. Read on.
What is the Dark Core Personality Test?
The dark core personality test is designed to measure the D-factor or the Dark factor, which is the underlying psychological construct connecting all dark personality traits. It reflects a person’s general tendency to maximize personal benefit even when it harms others or violates social norms.
According to darkfactor.org, the D-factor may be defined as – the general tendency to maximize one’s individual utility by disregarding, accepting, or malevolently provoking disutility for others, often accompanied by beliefs that serve as justifications.
Unlike traditional tests that emphasize strengths, this one explores how individuals prioritize self-interest, manipulate situations, or disregard ethical standards for personal gain. The goal is not to label individuals but to understand how these traits function and how awareness of them can lead to improved self-regulation, leadership, and ethical behavior.
This test is an advancement over the older dark triad framework, which assessed three independent traits: narcissism, Machiavellianism, and psychopathy. While the triad explains what dark traits look like, the D-factor explains why they exist. Both stemming from a shared belief that one’s goals and interests outweigh moral considerations.
The test typically consists of statements about interpersonal behavior, ethical reasoning, and self-interest. Respondents rate their agreement on a scale, and the results indicate their D-factor intensity. A higher score suggests stronger dark tendencies, such as manipulation, moral disengagement, or callousness. Lower scores represent individuals who value empathy, fairness, and integrity in their actions.
What Does the Dark Core Personality Test Measure?
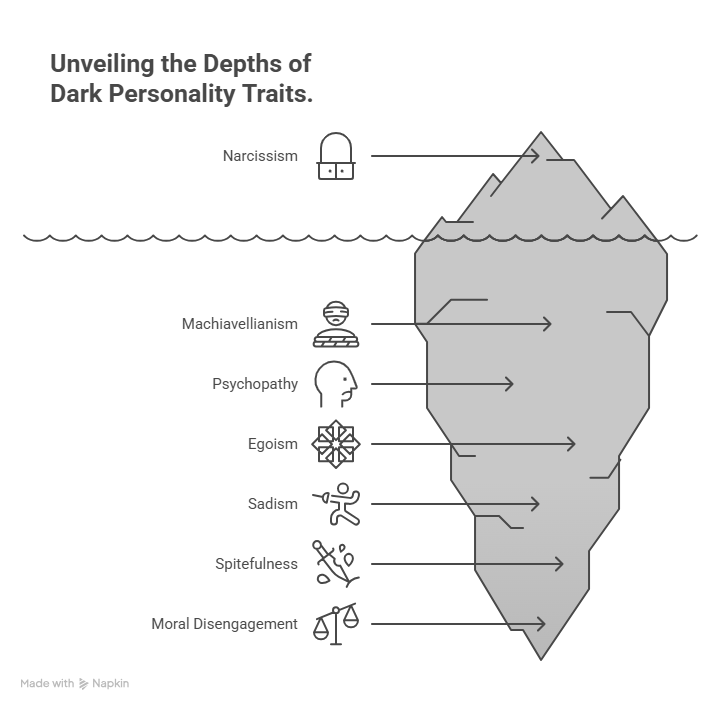
The dark core personality test measures the underlying psychological foundation that connects several socially undesirable traits. Rather than treating these characteristics as separate issues, it identifies how they emerge from the same motivational source known as the Dark Factor of Personality or D-factor.
Researchers acknowledge that the D-factor can be manifested in a large number of ethically, morally, and socially questionable attitudes and behaviors. Furthermore, they propose that any single dark trait will boil down to at least one of the defining features of the D-factor. For example, a person scoring high on narcissism might particularly be justifying the belief that they are superior. On the other hand, those scoring high in sadism may place a stronger emphasis on deriving utility from actively provoking disutility for others.
This shared foundation reflects a consistent pattern across individuals: the belief that personal goals and self-interest justify unethical, manipulative, or morally questionable behavior. People who score high on this factor tend to disregard social norms, empathy, and fairness when these stand in the way of achieving their objectives.
Below are the primary dark personality traits measured by the test. Each represents a unique way in which the same underlying mindset manifests in thought and behavior.
Narcissism
Narcissism involves an inflated sense of self-importance and an ongoing need for admiration and validation. Individuals with this trait often see themselves as exceptional and entitled to special treatment. They expect others to acknowledge their superiority and may react negatively to criticism or perceived disrespect.
In the context of the dark core, narcissism arises from ego-driven validation. It combines confidence with fragility, where self-worth depends on external recognition. In professional settings, narcissistic individuals can appear ambitious, charming, and persuasive. However, their competitiveness and sensitivity may lead to conflicts, exploitation, or poor collaboration.
When moderated by empathy, mild narcissism can inspire confidence and vision. When excessive, it becomes destructive, leading to arrogance, disregard for others, and manipulative self-promotion.
Machiavellianism
Machiavellianism reflects a calculating, manipulative approach to achieving goals. People high in this trait believe that the ends justify the means, often using deceit or strategic persuasion to get what they want. They tend to be highly analytical and emotionally detached, focusing on long-term gain rather than fairness or transparency.
In organizational environments, Machiavellian personalities can excel in negotiation and strategic planning, but they may use others as instruments for personal advancement. Their strength lies in foresight and tactical thinking, but their weakness lies in a lack of empathy and ethical concern.
The test measures this trait to assess how far individuals are willing to manipulate others or bend ethical rules for personal or professional advantage.
Psychopathy
Psychopathy is characterized by low empathy, impulsivity, and emotional coldness. Individuals with psychopathic traits are often fearless, confident, and unfazed by moral consequences. They can be charming and persuasive on the surface but display limited emotional connection or guilt.
In the dark core model, psychopathy represents emotional detachment and moral indifference. Such individuals might thrive in high-risk or high-pressure environments because they remain calm under stress. However, this same detachment can lead to reckless decision-making and exploitation of others.
Psychopathy is a critical element of the test because it helps distinguish between boldness rooted in confidence and impulsivity rooted in disregard for consequences.
Egoism
Egoism reflects an intense focus on personal benefit, often disregarding fairness, ethics, or others’ needs. Individuals high in egoism see life through a self-centered lens, believing that their success is paramount and that others’ well-being is secondary.
This trait reveals the moral belief that personal advancement justifies any action. In professional settings, egoistic individuals might prioritize recognition and reward over teamwork or ethical standards. While some degree of self-interest is healthy and motivates achievement, excessive egoism disrupts collaboration and erodes trust.
The test evaluates egoism to determine how an individual balances ambition with fairness and collective responsibility.
Sadism
Sadism refers to deriving pleasure or satisfaction from others’ discomfort, humiliation, or suffering. While often associated with extreme behaviors, sadistic tendencies can also appear subtly, such as enjoying others’ failures or using authority to intimidate.
In the dark core structure, sadism represents dominance through harm. It’s driven by the enjoyment of control and the emotional satisfaction that comes from exercising power over others. In professional environments, this can manifest as bullying, public criticism, or coercive leadership.
The test measures sadistic tendencies to identify potential risks in leadership behavior, workplace culture, and interpersonal interactions.
Spitefulness
Spitefulness is the willingness to harm others even when doing so brings no personal gain or may even cause personal loss. It is fueled by resentment, revenge, or a desire to assert control.
Spiteful individuals often act on emotional impulse rather than rational thought. They may undermine others, spread negativity, or deliberately damage relationships out of bitterness. While this behavior may provide short-term emotional relief, it often results in long-term personal and professional consequences.
Measuring spitefulness helps determine emotional stability, conflict management capability, and resilience. High levels can signal challenges in teamwork and stress management.
Moral Disengagement
Moral disengagement involves justifying unethical or harmful actions by reframing them as acceptable or harmless. Individuals high in this trait rationalize misconduct to preserve a positive self-image. For example, they might believe that lying or exploiting others is acceptable if it achieves a desirable outcome.
This cognitive process allows people to commit unethical acts without guilt or shame. In workplaces, it manifests when individuals overlook unethical practices because they are “good for business.” In leadership, moral disengagement can lead to rationalizing corruption, exploitation, or discrimination.
The test assesses this trait to evaluate how individuals perceive moral boundaries and whether they maintain ethical consistency under pressure.
Streamline your Pre-employment Assessments with Skillrobo
How These Traits Interconnect
Although each of these traits expresses itself differently, they all originate from the same underlying psychological foundation, which is the belief that self-interest justifies unethical behavior. This shared motivation binds them into one cohesive structure known as the D-factor.
A person high in narcissism may manipulate others for admiration, while someone high in Machiavellianism does it for control, and a psychopath does it for thrill or dominance. Despite these surface differences, their moral reasoning stems from the same psychological place: self-interest over ethics.
By measuring these interlinked traits, the dark core personality test provides a holistic view of human behavior. It helps psychologists and organizations identify not only specific tendencies but also the deeper patterns of moral flexibility and ethical risk that influence decision-making, leadership, and relationships.
The Psychology Behind The Dark Personality Core Test
At the core of the dark personality model lies one defining belief: the conviction that self-interest matters more than morality. Individuals with high D-factor scores often see rules and ethics as tools that apply to others but not necessarily to themselves.
This mindset, called moral flexibility, allows them to justify manipulative or harmful behavior as “necessary” or “deserved.” For example, someone might take credit for another’s work, convincing themselves that they “earned it.”
Psychologically, this behavior stems from reduced empathy and increased entitlement. People high in the dark core are often confident, ambitious, and persuasive. Although these traits may seem useful, they may also result in exploitation of others. Understanding these underlying motivations helps organizations, psychologists, and researchers predict behavioral risks and manage them effectively.
To understand the psychology behind the dark personality core test, let us look at a sample Dark Core Form:

How The Dark Core Personality Test Works
The dark core personality test typically features 50–100 statements measuring emotional control, moral reasoning, and interpersonal motives. Each statement is rated on a scale from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree.”
Common items might include:
- “I enjoy being in control of others.”
- “Rules exist to be broken when they limit progress.”
- “I don’t feel guilty when my actions help me succeed.”
Responses are scored to calculate:
- The D-factor (overall dark personality score)
- Sub-trait scores (narcissism, Machiavellianism, psychopathy, etc.)
- Behavioral patterns (how these traits manifest in real-world settings)
The dark core personality test free online version provides quick insights for self-awareness, while professional assessments used in psychology or recruitment offer validated, data-backed interpretations.
The Connection Between The Dark Core And The Dark Triad
The dark triad test was the foundation for studying negative personality traits, measuring narcissism, psychopathy, and Machiavellianism. However, it viewed these traits as separate, limiting the understanding of their shared origin.
The dark core personality test introduces a more cohesive model. Instead of examining behaviors in isolation, it identifies the D-factor that drives all dark traits. The triad focuses on what traits look like, while the dark core explains why they exist.
For instance, both narcissists and psychopaths may manipulate others, but for different reasons, one may seek admiration, while the other may seek control. The dark core unites these under a single framework: both prioritize personal gain over moral responsibility.
Dark Core Vs Dark Triad – Key Differences And Similarities
Although the dark triad and the dark core are related, they serve different purposes in personality assessment. The following table outlines their key distinctions and connections:
| Aspect | Dark Triad | Dark Core Personality (D-Factor) |
| Definition | A group of three socially undesirable traits: narcissism, psychopathy, and Machiavellianism. | A single psychological factor underlying all dark traits, explaining their shared foundation. |
| Focus | Measures specific negative traits separately. | Examines the unified motivation behind dark traits. |
| Scope | Narrower and trait-based. | Broader and motivational, encompassing more behaviors. |
| Theoretical Foundation | Focuses on external behavior patterns. | Focuses on internal moral beliefs and value systems. |
| Measurement Outcome | Scores for three independent traits. | One composite D-factor score with related sub-traits. |
| Purpose | Identifies personality tendencies that may influence social or professional interactions. | Explains the root cause of unethical, manipulative, or morally flexible behavior. |
| Use Case | Often used in personality profiling and leadership studies. | Commonly used in ethical risk assessment and psychological diagnostics. |
| Key Similarity | Both study socially aversive personality traits and their impact on human behavior. | Both provide insights into the darker dimensions of personality. |
The dark triad focuses on the manifestations of negative behavior, while the dark core focuses on the motivation. Understanding both provides a complete picture of an individual’s moral and behavioral profile.
The Grandiose Manipulative Factor Test and its Link to the Dark Core
The grandiose manipulative factor test examines traits of dominance, self-importance, and social control. These overlap heavily with narcissism and Machiavellianism, both rooted in the D-factor.
Such individuals are often persuasive, confident, and strategic, which are traits that can be advantageous in leadership. However, when combined with moral disengagement, they can become manipulative or exploitative.
The dark core personality test integrates these aspects, showing how grandiosity and control-seeking behaviors originate from the same underlying disposition. This helps in distinguishing between charismatic leadership and manipulative dominance in professional and social settings.
How to Use The Dark Core Personality Test
1. In Organizational Psychology
Organizations use dark core assessments to identify traits that may lead to toxic leadership, unethical decision-making, or workplace conflict. It helps HR teams predict potential behavioral risks, safeguard team culture, and select leaders who balance ambition with empathy.
2. In Clinical Psychology
Clinicians use the test to study antisocial tendencies, aggression, and moral disengagement. It offers insights into behavioral disorders and supports research into personality-based risk factors.
3. In Self-Development
For individuals, taking a personality test dark core enhances self-awareness. It highlights hidden behavioral drivers and supports personal growth by helping people recognize and regulate dark tendencies.
4. In Leadership Assessment
Leadership roles often magnify personality traits. The dark core test helps distinguish ethical assertiveness from manipulative dominance. It supports succession planning and ethical leadership development.
The Role Of Negative Traits in Personality Testing
Everyone has both light and dark traits. The negative traits test aspect of the dark core model acknowledges that dark characteristics aren’t always harmful. When balanced, they can promote resilience, confidence, and strategic thinking.
For instance, moderate narcissism may inspire charisma, while calculated Machiavellianism can foster strong negotiation skills. Problems arise when these traits dominate behavior unchecked. The dark core personality test doesn’t aim to suppress these traits but helps individuals and organizations manage them effectively.
Benefits Of The Dark Core Personality Test
The dark core personality test offers far-reaching insights into human behavior, ethics, and decision-making. By identifying the underlying psychological patterns that influence negative or manipulative tendencies, it provides both individuals and organizations with the ability to anticipate and manage behavioral risks.
1. Promotes Deep Self-Awareness
One of the most significant benefits of the dark core personality test is the level of introspection it encourages. Most individuals are unaware of how their darker traits manifest in everyday life. This assessment helps uncover hidden motivations.
By identifying these tendencies, individuals can reflect on how they affect relationships, decision-making, and personal growth. For example, a person who learns they score high in Machiavellianism might recognize a pattern of using manipulation instead of collaboration to achieve goals.
2. Improves Leadership and Ethical Decision-Making
Leaders play a pivotal role in setting organizational culture and ethical standards. The dark core test helps organizations identify leaders who possess manipulative, coercive, or morally disengaged tendencies that could damage team trust and company integrity.
By integrating dark core insights into leadership evaluations, companies can foster ethical decision-making and emotional intelligence at the executive level. For instance, a high D-factor score in a leadership candidate may prompt additional behavioral assessments to evaluate moral judgment and empathy.
3. Enhances Hiring Accuracy and Cultural Fit
Traditional hiring methods often focus on technical skills and experience, overlooking personality and behavioral risks. The dark core personality test bridges this skill gap by helping recruiters assess whether a candidate’s values align with the organization’s culture.
By identifying potential red flags, such as high narcissism, manipulativeness, or moral disengagement, organizations can prevent costly hiring mistakes. A single unethical or toxic employee can have a disproportionate impact on team morale, productivity, and brand reputation.
4. Predicts Ethical and Behavioral Risks
In corporate environments, ethical breaches, manipulation, and toxic behaviors can significantly affect organizational success. The dark core test provides a proactive way to assess the likelihood of such risks before they occur.
For example, individuals who score high in traits like Machiavellianism or psychopathy may excel in short-term performance metrics but later display unethical decision-making under pressure.
5. Supports Team Harmony and Interpersonal Understanding
Teams function best when members trust and respect one another. The dark core personality test helps identify personality conflicts and power dynamics that may disrupt collaboration.
For instance, if one team member exhibits narcissistic dominance while another demonstrates high spitefulness or low empathy, tension may escalate quickly. Recognizing these patterns early enables managers to structure teams effectively, assign roles strategically, and create an environment where differences are managed constructively rather than destructively.
6. Strengthens Organizational Integrity and Brand Reputation
A company’s reputation depends not just on its products or services but also on the ethical behavior of its employees. When organizations integrate dark core testing into their recruitment and leadership frameworks, they reduce the risk of unethical conduct, harassment, and workplace toxicity.
Companies known for integrity and psychological safety attract high-caliber talent and maintain better employee retention. The dark core personality test acts as a safeguard, ensuring that leadership and workforce behavior align with the company’s values.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|
| Helps identify individuals with potential for manipulative or unethical behavior | Candidates may manipulate responses to appear more favorable |
| Detects traits that can disrupt team dynamics and workplace trust | High scores can lead to unfairly negative perceptions |
| Assesses alignment between individual behavior and organizational values | Should not be used as the sole basis for hiring decisions |
| Supports ethical screening for leadership and management roles | Results may be misinterpreted without proper context or expertise |
| Highlights traits that may be beneficial in competitive or high-pressure roles | Ethical concerns around labeling individuals based on test outcomes |
Use Dark Core Personality Assessments in Skillrobo for Better Hiring Decisions
Skillrobo, a leading behavioral and skills assessment platform, incorporates dark core personality evaluations into its advanced psychometric suite. These tests assess psychological risk, integrity, and emotional stability, helping employers make informed, ethical hiring decisions.
With Skillrobo, organizations can:
- Detect early signs of manipulative or toxic leadership behavior.
- Combine dark core results with role-specific skill assessments for holistic profiling.
- Predict ethical alignment and decision-making patterns.
- Build psychologically safe, performance-driven teams.
Skillrobo’s behavioral analytics ensure that personality evaluation goes beyond surface-level attributes, providing a 360-degree view of professional compatibility. By integrating dark core assessments, organizations gain deeper insights into candidate authenticity, leadership trustworthiness, and workplace integrity.
Unlock the true potential of your workforce
How To Take The Dark Core Personality Test
Taking the dark core personality test typically takes 10–15 minutes. For best results:
- Choose a reputable testing platform like Skillrobo.
- Answer all statements honestly, based on real experiences.
- Avoid overthinking or giving “ideal” answers.
- Review your D-factor and sub-trait scores carefully.
- Use insights as a guide for personal or professional growth rather than a fixed label.
A balanced understanding of both strengths and dark traits leads to greater emotional intelligence and self-awareness.
Wrapping Up
The dark core personality test offers a profound understanding of the hidden drivers behind human behavior. It reveals how moral flexibility, self-interest, and manipulation connect under a single psychological factor, which is the D-factor. By identifying these tendencies, individuals and organizations can foster ethical awareness and behavioral control.
The dark core personality test, when implemented responsibly through intelligent platforms like Skillrobo, transforms from a psychological measure into a practical business tool, one that balances performance with ethics. Sign up for the free trial of Skillrobo to explore the effectiveness of the dark personality core test.
FAQs
1.What Is The Dark Core Personality Test?
It’s a psychological tool that measures the D-factor, revealing the underlying motivation behind negative traits like narcissism and manipulation.
2. Is The Dark Core Personality Test Free?
Yes, there are free online versions for personal use, but validated professional versions are more accurate for workplace or research applications.
3. How Is The Dark Core Related To The Dark Triad?
The dark triad explains individual dark traits, while the dark core reveals the single psychological foundation that drives them.
4. Which hiring platforms with dark triad personality tests are suited for remote team cultural fit assessment??
Skill assessment platforms like Skillrobo provide comprehensive dark trait assessment that can be used for cultural fir assessments during hiring.
5. Which online testing platforms provide validated dark core personality screening with anti-cheating features for remote hiring??
Skillrobo integrates dark core testing into its behavioral assessments along with anti-cheating features for hiring remote employees.